Введение
Несмотря на достигнутые успехи в борьбе с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями (ССЗ) атеросклеротического генеза, они по-прежнему остаются ведущей причиной смертности и инвалидизации населения многих стран, требуют колоссальных экономических затрат и представляют одну из главных угроз устойчивому мировому развитию в XXI в. [1–3].
Более четырех из пяти смертей от ССЗ происходят в результате инфаркта миокарда и инсульта, причем треть из этих случаев смерти носит преждевременный характер и отмечается среди людей в возрасте до 70 лет [4]. Согласно мнению экспертов ВОЗ, большинство преждевременных смертей от ССЗ может быть предотвращено путем изменения образа жизни (правильный рацион питания, прекращение употребления табака, уменьшение потребления соли, потребление фруктов и овощей, регулярная физическая активность, отказ от вредного употребления алкоголя). К сожалению, распространенность нездорового образа жизни высока в современном обществе (избыточный вес/ожирение, гиподинамия, табакокурение, злоупотребление алкоголем), а факторы сердечно-сосудистого риска недостаточно активно модифицируются, в т.ч. у пациентов, которые считаются подверженными высокому и очень высокому сердечно-сосудистому риску (ССР) [5, 6].
Факторы риска ССЗ
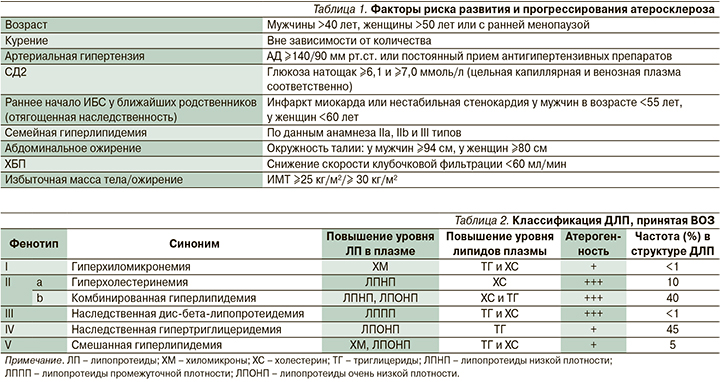
Первостепенное значение для снижения риска развития сердечно-сосудистых осложнений (ССО) и неблагоприятных исходов у пациентов с ССЗ имеет контроль кардиоваскулярных факторов риска (ФР; табл. 1) [1, 6, 7]. Крайне важно максимально раннее выявление и соответствующая коррекция имеющихся метаболических нарушений, особенно у лиц группы высокого риска (сахарный диабет 2 типа [СД2], артериальная гипертензия, атерогенная ДЛП, ожирение, хроническая болезнь почек [ХБП], неалкогольная жировая болезнь печени [НАЖБП]) [4, 7].
В РФ среди населения сохраняется высокая распространенность ФР, в т.ч. среди пациентов с очень высоким ССР [6]. Согласно исследованию EUROASPIRE, V, в популяции пациентов с очень высоким ССР на отдаленном этапе после перенесенных острого инфаркта миокарда, острого коронарного синдрома и/или вмешательств по реваскуляризации миокарда курить продолжали 18,5% российских пациентов, частота избыточной массы тела или ожирения составила 85,4 и 81,7%, абдоминального ожирения – 60,4 и 58,5%. Менее половины пациентов достигали уровня гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c) <7% (49,1% мужчин, 44,1% женщин) [8].
ДЛП признается ведущим ФР атеросклероза [6, 9–11]. Существуют различные виды ДЛП, которые могут быть обусловлены как приобретенными (вторичными), так и наследственными (первичными) состояниями.
В соответствии с классификацией Д. Фредриксона (ВОЗ, 1970) выделяют следующие фенотипы гиперлипопротеинемий с присущими каждому из них частотой, определенными соотношениями различных классов липидов, липопротеидов и вкладом атерогенности (табл. 2) [12]. Согласно оценкам, более половины взрослого населения во всем мире страдают ДЛП; широко распространенным нарушением липидного профиля является смешанная (комбинированная) атерогенная ДЛП [11, 13–15].
В настоящее время для оценки прогноза и эффективности лечения сохраняет ведущую роль ХС-ЛПНП. Этот показатель является основной мишенью липидснижаюшей терапии, а достижение целевого уровня ХС-ЛПНП – ключевое условие улучшения течения и прогноза у пациентов с ССЗ [1, 15]. Снижение уровня ХС-ЛПНП на каждые 1,0 ммоль/л соответствует снижению заболеваемости и смертности, связанных с ССЗ, на 22%. Вместе с тем, согласно исследованию EUROASPIRE, V, частота достижения целевого уровня ХС-ЛПНП пациентами с ишемической болезнью сердца (ИБС), получающими гиполипидемическую терапию, остается низкой как в России (30,2%), так и в общей популяции исследования (32,0%), что, по-видимому, свидетельствует об использовании недостаточно эффективных препаратов, недостаточных доз лекарственных средств и редком назначении комбинированной гиполипидемической терапии [8, 16].
Сахарный диабет 2 типа как фактор риска ССЗ
К сожалению, в современном обществе отмечается значимый рост распространенности таких существенных ФР ССЗ, как СД2 и избыточная масса тела/ожирение (табл. 2) [6, 14, 17, 18]. По данным Федерального регистра СД, в РФ на 01.01.2022 состояли на диспансерном учете 4 871 863 человека (3,34% населения), из них 92,3% (4 498 826) с СД2 [19]. ССР возрастает уже на этапе ранних нарушений углеводного обмена, согласно данным исследования NATION, в РФ численность таких пациентов с преддиабетом составила более 20,7 млн (19,3%) [20]. СД2 приводит к раннему развитию, увеличивает тяжесть, ухудшает течение, видоизменяет клинические проявления ССЗ; типично распространенное поражение всего сосудистого русла [11, 18, 21]. Смертность от ССЗ у пациентов с СД2 в 2–4 раза выше, чем у пациентов с нормогликемией; 80% летальных исходов обусловлены проявлениями атеросклероза, а ¾ из них – ИБС. Важно отметить, что при СД2 безболевая («немая») ишемия миокарда наблюдается в 2–7 раз чаще, чем у пациентов с нормальной толерантностью к глюкозе [21, 22].
Высокая распространенность сердечно-сосудистой патологии у больных СД2 обусловлена совокупным воздействием инсулинорезистентности, хронической гипергликемии и ассоциированных с ними метаболических нарушений: гиперинсулинемии, неферментативного гликирования белков, липотоксичности, ДЛП, накопления свободных радикалов конечных продуктов окисления, хроническим воспалением, ранним развитием эндотелиальной дисфункции и пр. [11, 14, 18, 23]. Инсулинорезистентность нарушает системный метаболизм липидов, включая постпрандиальный период, и приводит к развитию вторичной ДЛП: гипертриглицеридемия (ГТГ), низкий уровень липопротеидов высокой плотности (ЛПВП) и появление мелких плотных ЛПНП. Атерогенная ДЛП очень часто встречается у пациентов с СД2, ее распространенность составляет 72–85%, что еще больше повышает риск сердечно-сосудистых событий [11, 14, 24]. С учетом растущей распространенности СД во всем мире эффективное лечение ДЛП наряду с контролем гликемии и артериального давления может снижать риск ССЗ у таких пациентов.
ССР в общей популяции оценивается по шкале SCORE – системной оценке коронарного риска (Systemic Coronary Risk Evaluation). В современных рекомендациях подчеркивается, что больные документированным ССЗ, СД1 или 2, очень высокими уровнями отдельных ФР или с ХБП, как правило, имеют очень высокий или высокий риск ССЗ, для них оценки риска по шкале SCORE не требуется.
В частности, больные СД с атеросклеротическими ССЗ (АССЗ) или ХБП С3–5 или протеинурией или с большими ФР (курение, выраженная гиперхолестеринемия, выраженная артериальная гипертензия) относятся к группе очень высокого ССР. Большинство остальных больных СД (за исключением молодых больных СД1 без основных ФР) относятся к группе высокого ССР. Молодые больные СД1 без основных ФР относятся к группе среднего ССР [10, 12, 19].
В соответствии с положениями 10-го выпуска Алгоритмов специализированной медицинской помощи больным сахарным диабетом [19] целевые уровни показателей липидного обмена представлены в табл. 3.

Показатели липидного профиля и риск атеросклероза
Коррекция ДЛП в первую очередь должна быть сосредоточена на снижении уровня ХС-ЛПНП (табл. 4). ССР четко возрастает с увеличением уровня ХС-ЛПНП и продолжительности его неблагоприятного воздействия на сосудистую стенку. Доказана прямая зависимость между уровнем ХС и ХС-ЛПНП в крови и смертностью от ИБС, что подчеркивает важность оптимального контроля начиная с раннего возраста, когда только инициируется процесс атероматоза, а его прогрессирование клинически проявляется как АССЗ в среднем возрасте или в более поздние годы [1, 16, 25].

Многочисленные клинические исследования показали, что снижение уровня ХС-ЛПНП может способствовать снижению риска ССО, в т.ч. и у пациентов с СД2 [14, 25, 26]. Целевой уровень ХС-ЛПНП зависит от категории риска пациента, что необходимо учитывать на практике (табл. 4) [10, 15].
Помимо ХС-ЛПНП в развитие связанных с атеросклерозом ССЗ значимый вклад вносят липопротеиды, содержащие аполипопротеин В (апоB), в т.ч. богатые ТГ липопротеиды и их ремнанты (ЛПОНП, хиломикроны) [1, 9, 11, 27]. ГТГ существенно дополняет механизмы, влияющие на атерогенез, и увеличивает частоту ССЗ на 32% у мужчин и на 76% у женщин [28].
ГТГ способствует повышенному риску ССЗ как непосредственно, так и потому, что она ассоциируется с такими ФР, как ожирение, метаболический синдром, СД2, НАЖБП. ГТГ является этиологическим фактором острого панкреатита, риск развития которого увеличивается при уровне ТГ более 10 ммоль/л [9, 14].
Ключевой механизм атерогенеза при ГТГ заключается в чрезмерном образовании в печени частиц ЛПОНП. Происходит перенос ТГ из ЛПОНП в ЛПНП и одновременно с этим перемещение эфиров ХС из ЛПНП в ЛПОНП. Таким образом, инициируется еще один путь атеросклеротического процесса: ЛПОНП, потерявшие часть ТГ в обмен на ХС, становятся более мелкими, что значительно повышает их способность проникать в стенку сосуда [9, 11, 15]. Тесную связь с прогрессированием атеросклеротического процесса имеют высокие постпрандиальные уровни ТГ (свойственные пациентам с инсулинорезистентностью, ожирением, СД2), что опосредовано усилением захвата окисленных ЛПОНП клетками сосудистой стенки, накоплением их в макрофагах и уменьшением протективного эффекта ЛПВП [28].
Наряду с этим у пациентов с атерогенной смешанной ДЛП повышено содержание мелких плотных ЛПНП, которые из-за малых размеров намного легче проникают в сосудистую стенку, более подвержены перекисному окислению, не связываются с ЛПНП-рецепторами печени, следовательно, медленнее элиминируются из кровотока, приводя к ускорению атерогенеза, способствуют развитию дисфункции эндотелия, а за счет увеличения синтеза тромбоксана повышают активность тромбоцитов [1, 12, 27]. При уровне ТГ 1,7–2,3 ммоль/л следует проводить немедикаментозную терапию. Фармакотерапию следует начинать пациентам с уровнем ТГ >2,3 ммоль/л [9]. Содержание ХС-ЛПВП обратно пропорционально риску АССЗ. ЛПВП играют важную роль в предотвращении накопления избытка ХС в тканях, осуществляя обратный транспорт ХС, при котором происходит перенос ХС от периферических тканей (в т.ч. артериальных стенок артерий) в печень, откуда он элиминируется в составе желчных кислот. Факторы, влияющие на содержание ЛПВП в плазме, перечислены в табл. 5.

Однако до сих пор нет четких доказательств того, что рост уровня ХС-ЛПВП в плазме снижает риск ССЗ, тем не менее этот показатель является полезным биомаркером для уточнения оценки риска с использованием шкалы SCORE2 [10, 12].
Гиполипидемическая терапия. Липидснижающая эффективность, механизм действия статинов
Достижение целевого уровня ХС-ЛПНП является первостепенной задачей гиполипидемической терапии, направленной на снижение ССР. Эффективное лечение АССЗ трудно представить без применения ингибиторов 3-гидрокси-3-метилглютарил-коэнзим А-редуктазы (ГМГ-КоА-редуктазы) или статинов – наиболее изученного класса гиполипидемических средств, занимающих лидирующие позиции в современных руководствах в качестве терапии первой линии. Статины являются основой первичной и вторичной профилактики атеросклероза; причем относительное снижение риска при первичной профилактике сопоставимо с таковым во вторичной профилактике [10, 16, 30].
Наиболее существенно статины снижают уровень ХС-ЛПНП, тем самым снижая заболеваемость, смертность от АССЗ и необходимость вмешательства на коронарных артериях [10, 31–33]. В меньшей степени ингибиторы ГМГ-КоА-редуктазы влияют на содержание ТГ и ХС-ЛПВП: уменьшают на 10–20%, повышают на 8–10% от исходных значений соответственно [10, 31]. Клиническая эффективность липидснижающей терапии определяется достигнутым уровнем ЛПНП, при этом ожидаемое снижение в ответ на терапию статинами может широко варьироваться у пациентов [15, 29, 33]. Крупный мета-анализ 19 исследований (n=56 934) с применением различных препаратов группы статинов показал снижение смертности от всех причин на 14% (отношение шансов [ОШ]=0,86; 95% доверительный интервал [ДИ]: 0,79– 0,94), частоты сердечно-сосудистых событий на 25% (ОШ=0,75; 95% ДИ: 0,70–0,81), нефатальных и фатальных коронарных осложнений на 27% (ОШ=0,73; 95% ДИ: 0,67–0,80), инсульта на 22% (ОШ=0,78; 95% ДИ: 0,68–0,89) при снижении уровня ХС-ЛПНП на 1,0 ммоль/л [34].
Известно, что превращение ГМГ-КоА в мевалонат под действием ГМГ-КоА-редуктазы в гепатоцитах является начальной и лимитирующей стадией биосинтеза ХС. Обладая сходством в строении с ГМГ-КоА-редуктазой, статины, связываясь с активным центром, конкурентно ингибируют этот фермент, что приводит к конформационным изменения в его структуре [35]. Согласно механизму обратной связи, уменьшение уровня внутриклеточного ХС способствует увеличению экспрессии рецепторов ЛПНП на поверхности гепатоцитов, соответственно, ускорению катаболизма ХС-ЛПНП [36, 37]. Это влечет за собой увеличение захвата частиц ЛПНП из крови и уменьшение концентрации в плазме ЛПНП и других апо В-содержащих липопротеины, включая частицы, в составе которых есть ТГ. Наряду со снижением уровня ХС-ЛПНП ингибиторы ГМГ-КоА-редуктазы усиливают процесс катаболизма ЛПОНП и ЛППП, в составе которых есть ТГ [36, 38].
Необходимо отметить негиполипидемические (плейотропные) эффекты статинов, в числе которых противовоспалительное, антипролиферативное, антитромботическое, антиоксидантное действия; способность устранять дисфункцию эндотелия, подавлять экспрессию клеточных молекул адгезии, которые, несомненно, существенны для профилактики ССЗ [38, 39]. Прием статинов приводит к небольшому увеличению уровня ХС-ЛПВП (механизм окончательно не изучен). Предполагают, что подобный эффект может быть обусловлен ингибированием активности белка, переносящего эфиры ХС, а также уменьшением количества частиц ЛПОНП и ЛПНП в плазме крови вследствие их усиленного катаболизма [31, 36]. Терапия статинами безопасна и, как правило, хорошо переносится [15, 16].
Клинические преимущества розувастатина
Ингибиторы ГМГ-КоА-редуктазы существенно различаются по способности снижать концентрацию атерогенных липидов в крови. Химическая структура розувастатина с наличием стабильной полярной метансульфамидной группы обеспечивает высокую гидрофильность и увеличивает сродство молекулы к ГМГ-КоА-редуктазе, следствием чего является более выраженная липидснижающая активность розувастатина по сравнению с другими представителями этого класса препаратов [16, 39, 40]. Гиполипидемический эффект розувастатина в 2 раза выше, чем аторвастатина, и в 4 раза выше, чем симвастатина.
Конечный период полувыведения розувастатина самый продолжительный среди статинов (около 19 часов); элиминация происходит главным образом печенью. Розувастатин – это гидрофильный препарат с высокой гепатоселективностью, низкой системной биодоступностью, следствием чего является ограниченное его проникновение во внепеченочные ткани, следовательно, более низкий риск миотоксичности. Розувастатин практически не взаимодействует с системой цитохрома-Р450 (и его изоферментом 3А4), что снижает вероятность неблагоприятных межлекарственных взаимодействий [39, 40]. Клинический опыт применения розувастатина демонстрирует, что препарат имеет наилучший профиль безопасности среди статинов [39, 41].
В клинических исследованиях гиполипидемической эффективности статинов в разных популяциях пациентов (с ИБС, острым инфарктом миокарда в анамнезе, цереброваскулярными заболеваниями, заболеваниями периферических сосудов, СД2) определено значимое превосходство розувастатина в диапазоне различных доз в снижении концентрации ХС-ЛПНП по сравнению с аторвастатином, симвастатином, правастатином [39, 42–44]. В частности, согласно результатам исследования STELLAR (Statin Therapies for Elevated Lipid Levels compared Across doses to Rosuvastatin) с участием 2431 пациента с ДЛП применение розувастатина (10–80 мг/сут) привело к снижению уровня ХС-ЛПНП на 8, 26 и 12–18% больше по сравнению с применением аторвастатина (10–80 мг), правастатина (10–40 мг/сут), симвастатина (10–80 мг) соответственно (р<0,001). В группе терапии розувастатином в режиме высокой интенсивности снижение уровня ЛПНП составило 52–63% (рис. 1) [42].

Существенное для клинической практики преимущество над другими представителями класса статинов заключается в том, что уже в стартовой дозе 10 мг розувастатин позволяет достигать целевого уровня ЛПНП [39, 42, 43]. Причем высокая липидснижающая активность стартовой дозы розувастатина (10 мг) отмечена и в особых группах пациентов с СД2, ожирением и метаболическим синдромом [44]. Подбирая конкретный препарат из группы статинов, следует учитывать, что на фоне приема розувастатина (даже в начальной дозе) вероятность длительного удержания уровня ХСЛПНП в более низком диапазоне значений существенно возрастает [39].
Помимо высокой липидснижающей активности розувастатин доказанно улучшает прогноз и признается наиболее эффективным препаратом как первичной, так и вторичной профилактики ССЗ среди статинов [16, 39, 40, 45]. Одним из доказательств эффективности и безопасности розувастатина в первичной профилактике ССЗ при исходно невысоким уровне ХС-ЛПНП стали результаты исследования JUPITER с участием 17 802 пациентов без признаков ССЗ (из них 41% пациентов с метаболическим синдром, 16% курящих пациентов, 57% с артериальной гипертензией). Исследование завершилось досрочно через 1,9 года в связи с бесспорной эффективностью розувастатина (20 мг/сут); показано значимое снижение частоты неблагоприятных клинических исходов, включая смертность, на фоне снижения ХС-ЛПНП до среднего уровня 1,42 ммоль/л (на 50%) и С-реактивного белка до 2,2 мг/л (на 37%). Важно помнить, что уровень высокочувствительного СРБ >2 мг/л считается независимым предиктором ССО, обусловленных атеросклерозом. По результатам исследования отмечено снижение вероятности развития первичной комбинированной конечной точки (острый инфаркт миокарда, инсульт, нестабильная стенокардия, реваскуляризация, сердечно-сосудистая смертность) на 44% (ОШ=0,56; 95% ДИ: 0,46–0,69, р<0,00001) и вторичной конечной точки (смертность от всех причин) на 20% (ОШ=0,80; 95% ДИ: 0,67–0,97, р<0,02) по сравнению с плацебо [46].
Атерогенная дислипидемия и остаточный липидный риск ССО
Использование статинов позволяет минимизировать риски ССЗ у пациентов с атерогенными ДЛП, хотя при достижении целевого уровня ХС-ЛПНП у ряда пациентов сохраняется остаточный (резидуальный) риск ССО и происходят тяжелые сосудистые события, ухудшение течения основного ССЗ [18, 45–47]. Считается, что частично это связано с неадекватным снижением уровня ХС-ЛПНП для данного уровня риска пациента, высоким уровнем ТГ и/или низким содержанием ХС-ЛПВП, иначе говоря, существует необходимость в оптимизации дополнительных целей при лечении ДЛП.
Остаточный липидный риск усугубляется постоянно растущим числом лиц с выраженными метаболическими нарушениями, инсулинорезистентностью (ожирением, метаболическим синдромом, СД2) и комбинированной атерогенной ДЛП [9, 11, 14, 18, 48]. Немаловажная причина остаточного риска – ГТГ; атерогенный риск, связанный с частицами, богатыми ТГ и их ремнантами, приближается к риску, вызванному ХС-ЛПНП [9, 49, 50]. Так, согласно данным Фремингемского исследования, уровень ТГ >1,7 ммоль/л достоверно связан с повышенной вероятностью развития ССО [51].
Поэтому, чтобы избегать негативного влияния на кардиоваскулярный прогноз атерогенных фенотипов ДЛП, а также для выбора оптимальной терапевтической стратегии, рекомендуется анализировать изменения в липидном спектре крови пациента в целом, включая оценку уровня ТГ у лиц с высоким, очень высоким и экстремальным ССР в рутинной практике [9, 45]. К сожалению, атерогенная ДЛП недостаточно хорошо диагностируется, что продемонстрировано в исследовании реальной клинической практики EURIKA (European Study on Cardiovascular Risk Prevention and Management in Usual Daily Practice) [52]. Среди участников исследования без ССЗ (n=7641, 51,6% женщин) в возрасте >50 лет с наличием по крайней мере одного сердечно-сосудистого ФР, ГТГ (ТГ ≥ 2,3 ммоль/л) выявлена в 21% случаев, пониженный уровень ХС ЛПВП (менее 1,0 ммоль/л у мужчин и менее 1,3 ммоль/л у женщин) – в 22%, а комбинация отмеченных нарушений почти у 10% этой когорты. Причем более половины лиц с подобными атерогенными сдвигами не получали липидоснижающую терапию.
Среди причин высокого резидуального липидного риска выделяют низкую эффективность статинов, что может быть обусловлено метаболизмом ХС, побочным действием их высоких доз, повышением активности пропротеинконвертазы субтилизин/кексин 9-го типа, нежелательными лекарственными взаимодействиями с другими препаратами (изоформы цитохрома-P450 3A4), полиморфизмом генов, влияющих на метаболизм липидов [54]. В такой ситуации увеличение дозы статинов не всегда оправданно с точки зрения снижения содержания ХС-ЛПНП и опасно увеличением частоты нежелательных эффектов.
На снижение остаточного риска и достижение наилучшего прогноза направлена комбинированная липидснижающая терапия [10, 41, 45, 50]. Действующие рекомендации при выявлении ГТГ нацеливают на назначение статинов, а при недостижении целевого уровня ТГ – на добавление к терапии фибратов [9, 10, 15], которые эффективно снижают в крови не только уровень ТГ натощак, но и содержание ТГ и богатых триглицеридами ремнантов в постпрандиальном периоде [18, 49, 53].
Клинические преимущества фенофибрата
Фибраты являются основной группой гиполипидемических препаратов, активно воздействующих на уровень ТГ крови, в т.ч. в условиях хронической гипергликемии и ДЛП. Уменьшение уровня ТГ является важной составляющей снижения ССР [9]. Фибраты особенно эффективны для пациентов с СД2, лиц с инсулинорезистентностью, абдоминальным ожирением и другими проявлениями метаболического синдрома и достоверно снижают риск ССО [9, 54, 56].
В качестве важного компонента лечения ДЛП в сочетании с ингибитором ГМГ-КоА-редуктазы обоснованно применение фенофибрата, обладающего высокой липидснижащей эффективностью и рядом дополнительных плейотропных эффектов. Фенофибрат – единственный препарат данного класса, зарегистрированный в Российской Федерации. Фенофибрат достоверно снижает уровень ТГ на 50%, уровень ЛПНП примерно на 25%, одновременно повышая значения ЛПВП на 10–30%, что потенциально полезно для снижения резидуального риска у некоторых пациентов [9, 45, 56].
Механизм действия фибратов опосредован активацией факторов транскрипции генов – внутриклеточных (ядерных) рецепторов PPARα (альфа-рецепторы, активируемые пролифератором пероксисом), что ведет к пролиферации пероксисом – специфических внутриклеточных органелл, регулирующих катаболизм жирных кислот, продукцию апо C-III и аполипопротеинов AI/AII. Модулируя активность PPARα, фенофибрат воздействует на метаболизм липидов посредством нескольких механизмов [41, 57, 58]. Путем активации липопроинкиназы (фермент, осуществляющий гидролиз частиц, богатых ТГ) и уменьшения синтеза апо С-III происходит усиление липолиза и выведение из плазмы крови атерогенных липопротеидов с высокой концентрацией ТГ (ЛПОНП, хиломикроны). Кроме того, фенофибрат повышает клиренс ХС-ЛПНП и снижает концентрацию высокоатерогенных мелких плотных частиц ЛПНП, апо В; высокое содержание которых характерно для пациентов с атерогенным профилем, опасным в плане риска развития сердечно-сосудистых событий [9, 56]. Кроме того, активация PPARα приводит к увеличению концентрации фракции ЛПВП посредством повышения экспрессии генов аполипопротеинов AI/AII и к снижению переноса ХС из ЛПВП в ЛПОНП [9, 56, 57]. Конечным результатом является уменьшение атерогенности липидного спектра крови (табл. 6).

Помимо влияния на обмен липидов фенофибрат снижает уровень мочевой кислоты, улучшает функцию эндотелия, оказывает противовоспалительное действие. Хроническое воспаление рассматривается как один из ключевых факторов развития атеросклероза [1, 10, 53].
Противовоспалительные и антиоксидантные свойства препарата реализуются за счет снижения образования медиаторов воспаления (С-реактивного белка, фактора некроза опухоли-α, интерлейкинов-1β, -6), перекисного окисления липидов и образования активных форм кислорода.
Значимым сосудистым эффектом препарата является снижение активность молекул адгезии, синтеза факторов прокоагуляции (фибриноген, активатор ингибитора плазминогена-1), что благоприятно сказывается на вероятности развития атеротромботических событий [41, 58].
Существуют работы, указывающие на благотворное влияние фенофибрата, связанное с предотвращением прогрессирования НАЖБП, которая является независимым ФР ССЗ, ассоциированных с атеросклерозом [59].
Гиполипидемическая эффективность фенофибрата нашла свое подтверждение в клинических исследованиях, мета-анализах, в которых продемонстрировано снижение риска больших сердечно-сосудистых событий, микрососудистых осложнений и улучшение прогноза у пациентов с атерогенной ДЛП [9, 57, 60].
В исследовании FIELD (Fenofibrate Intervention and Event Lowering in Diabetes) продемонстрирована не только липидснижающая эффективность фенофибрата, но и его способность предотвращать макро- и микрососудистые осложнения у пациентов с СД2 вне зависимости от уровня HbA1c. Монотерапия фенофибратом в течение 5 лет значимо улучшила сердечно-сосудистый прогноз. Так, в группе фенофибрата по сравнению с группой плацебо отмечено достоверное уменьшение (на 24%) риска нефатального инфаркта миокарда (р=0,010), на 11% в целом всех сердечно-сосудистых событий (р=0,035) и на 21% необходимости в проведении коронарной реваскуляризации (р=0,035)). Важно отметить, что на фоне терапии фенофибратом показано уменьшение потребности в ампутациях на 47%, на 37% в лазерной коагуляции сетчатки, на 79% замедление прогрессирования диабетической ретинопатии, на 18% снизился риск развития нефропатии, что безусловно является следствием уменьшения выраженности микроваскулярных осложнений СД [61]. Доказана способность фенофибрата снижать риск диабетических сосудистых осложнений.
Большой интерес представляет исследование DIAS (Diabetes Atherosclerosis Intervention Study), в котором изучалось влияние фенофибрата на прогрессирование коронарного атеросклероза у больных СД2 с помощью повторной количественной ангиографии. Применение фенофибрата сопровождалось замедлением атеросклеротического поражения коронарных артерий (рис. 2): среднее увеличение степени стеноза составило 2,11±0,594%, что на 42% меньше, чем в группе плацебо (3,65±0,608%, p=0,02). Кроме того, в группе фенофибрата по сравнению с плацебо наблюдалось снижение среднего диаметра сегмента коронарного русла, а увеличение стеноза по отношению к исходному уровню было менее выраженно на 25% (р=0,171) и 42% (р=0,020) соответственно. Отмеченные положительные изменения ангиографической картины происходили на фоне достоверного снижения концентраций атерогенных показателей (на 56% ТГ, на 25% общего ХС, на 32% ХС-ЛПНП) и увеличения уровня ХС-ЛПВП на 11–34% (p<0,001 для всех значений). В исследовании DIAS доказано, что наряду со снижением уровня ТГ и повышением уровня ХС-ЛПВП фенофибрат снижает концентрацию мелких плотных частиц ЛПНП [62]. Существенное улучшение липидного метаболизма наблюдается при комбинации фенофибрата со статинами по сравнению с их монотерапией.

Фиксированная комбинация розувастатина и фенофибрата
Существенное улучшение показателей липидного профиля наблюдается при комбинации фенофибрата со статинами по сравнению с монотерапией этими препаратами. В РФ зарегистрирована фиксированная комбинация (ФК) розувастатина (10 мг) и фенофибрата (145 мг) [63]. Повышение приверженности к фармакотерапии – один из реальных способов повышения ее эффективности, поэтому использование ФК является приоритетным направлением в лечении различных заболеваний. В связи с ростом распространенности коморбидных состояний, большим количеством одновременно принимаемых лекарственных средств, что во многом затрудняет проведение фармакотерапии, ФК розувастатина и фенофибрата выгодна с точки зрения гиполипидемической эффективности, безопасности и клинических преимуществ [41, 45, 64]. Применение ФК розувастатина и фенофибрата возможно при необходимости одновременного приема розувастатина и фенофибрата в соответствующих дозах и предпочтительно для пациентов с гиперхолестеринемией и ГТГ для улучшения результатов лечения и прогноза АССЗ, повышения приверженности пациента к терапии.
Липидснижающие эффекты розувастатина и фенофибрата обусловлены разнонаправленными механизмами воздействия и разными терапевтическими мишенями, что обеспечивает многоцелевые взаимодополняющие эффекты на атерогенную ДЛП и достижение наибольшего плейотропного эффекта. В частности, розувостатин значимо снижает содержание ХС-ЛПНП в крови, влияние фенофибрата на этот показатель спектра липидов значительно меньше; терапия фибратами по сравнению со статинами в большей степени снижает уровень ТГ и повышает содержание ХС-ЛПВП в крови, что в совокупности обеспечивает общий потенциал гиполипидемического воздействия совместного применения.
Положительный профиль эффективности и безопасности фенофибрата и розувастатина, в т.ч. в составе ФК, продемонстрирован в различных исследования. Назначение ФК фенофибрата и розувастатина, обладающей всеми преимуществами обоих компонентов, входящих в состав комбинации, может дополнительно улучшить контроль липидов, снизить остаточный риск у пациентов с АССЗ, в т.ч. при сочетании с СД2 [41, 64–66]. Использование комбинированной гиполипидемической терапии определяет необходимость регулярного контроля безопасности проводимого лечения. При совместном использовании статинов и фибратов контроль активности креатинфосфокиназы выполняется каждые 3 месяца первого года терапии независимо от наличия жалоб на мышечную боль или слабость. Уровень аланинаминотрансферазы и креатинина мониторируют каждые 6 месяцев [66].
Заключение
Атеросклероз является прогрессирующим заболеванием с задействованием множества ФР и патофизиологических механизмов. Одним из главных ФР ССЗ выступает атерогенная ДЛП. Контроль содержания атерогенных липидов зачастую остается неудовлетворительным. Для улучшения профилактики и прогноза АССЗ необходимо использовать все имеющиеся фармакологические возможности с многоцелевым воздействием на ДЛП, включая совместное применение розувастатина и фенофибрата в виде ФК.



