Введение
По статистике Всемирной организации здравоохранения (ВОЗ), в 2019 г. рак занял первое или второе место по значимости причины смерти в 112 странах мира и третье или четвертое еще в 23 странах [1, 2]. В странах с более высоким уровнем экономического развития снижается смертность от инсульта и ишемической болезни сердца, а рак становится основным и единственным заболеванием, снижающим продолжительность жизни [1, 3]. Из-за роста и старения населения пока не наблюдается существенной тенденции к снижению заболеваемости основными видами рака высокого риска, а в некоторых странах их бремя быстро возросло. Это отражает изменения в распространенности и распределении основных факторов риска, связанных с социально-экономическим развитием [4, 5]. Сто лет понадобилось для того, чтобы рак распространился по всему миру. Это связано с изменениями образа жизни, привычек и увеличением продолжительности жизни человека, а также с повышением уровня диагностируемости злокачественных новообразований. Рак является одним из самых страшных заболеваний XX в., и в XXI в. его заболеваемость продолжает распространяться и увеличивается. Ситуация настолько тревожная, что каждый четвертый человек в течение жизни подвергается риску заболевания раком [6, 7]. Мы постоянно подвергаемся воздействию различных агентов, вызывающих рак, известных как канцерогены. Что такое рак? Рак – это аномальный, неконтролируемый рост клеток. Место локализации рака может быть в любом органе или структуре тела. Диагностика рака может носить случайный характер при лабораторном или рутинном радиологическом тесте при обычной диспансерицзации или в случае, когда распространение его в теле пациента уже дает видимые причины для беспокойства [6]. Трансформация нормальной клетки в раковую происходит из-за неспособности собственных иммунных клеток организма идентифицировать и уничтожить вновь образовавшиеся раковые клетки, когда их немного [6–8]. Риск рака увеличивается у тех людей, чья иммунная система подавлена каким-либо фактором, включая хронический стресс, старость, хронические изнурительные заболевания, предыдущее использование химиотерапии и злоупотребление такими лекарствами, как анальгетики, антибиотики и кортикостероиды [6]. Таким образом, целью данного исследования является проведение клинико-статистического анализа в области диагностики новых случаев онкологических заболеваний, летального исхода и эффективности применения современных методов терапии, диагностики рака. Основное внимание уделялось методам, которые показали наибольшую эффективность в раннем выявлении опухолей. Согласно данным, полученным от ведущих онкологических центров страны, было выявлено, что некоторые методы, такие как цитологический скрининг рака шейки матки, демонстрируют высокую эффективность в раннем выявлении заболевания. Также были рассмотрены выявления онкологических заболеваний, которые включают в себя различные этапы диагностики, начиная от первичного обследования и заканчивая более сложными методами диагностики, что позволяет оптимизировать процесс выявления заболеваний и повысить шансы на успешное лечение.
Материалы и методы
Данная стратегия поиска информации была адаптирована из публикации Roseleur J. et al. [9] для определения типов обследования и лечения онкологических заболеваний людей, у которых был когда-либо в мире диагностирован рак. Стратегия поиска была направлена на выявление соответствующих исследований, опубликованных в MEDLINE, PubMed и Scopus, и включала медицинские предметные рубрики, а также соответствующий текст (название и аннотация), а также поиск по ключевым словам с использованием терминов для описания населения и терминов, нуждающихся в поддерживающем уходе. Стратегия поиска была направлена на выявление всего спектра типов в диагностической, лечебной и поддерживающей терапии путем включения синонимов для конкретных этапов лечения онкологических заболеваний. Построение графиков осуществлялось с помощью программы Microsoft Excel 2013.
Результаты и обсуждение
Распространенность различных видов рака
В настоящее время между регионами и странами существуют различия в заболеваемости и смертности от рака, главным образом, за счет различия в факторах популяционного риска, вызванных социально-экономическими изменениями. В публикации Lin L. описано, что в 2019 г. от рака умерло более 10 млн человек, что вдвое больше, чем в 1990 г., а заболели 23 миллиона человек. По данным онкологических исследований за 2019 г., раком с самым высоким уровнем смертности были рак трахеи, бронхов и легких, рак толстой и прямой кишки, а также рак желудка. Число смертей от этих видов рака составило в среднем 2 042 640, 1 085 797 и 957 185 соответственно, что составило 40,8% всех смертей от рака в 2019 г. [1].
По открытым данным на 2020 г. было зарегистрировано около 20 млн случаев злокачественных новообразований, число летальных исходов достигло 10 миллионов человек. При анализе статистических данных выявлено, что большая часть онкологических заболеваний распространена на территории Азии. Второе место по распространенности онкозаболеваний занимает Европа, далее Америка. Азия стала лидером в распространении онкологических заболеваний, так как на ее территории проживает большая часть населения, в соответствии с этим там отмечено различное распределение типов злокачественных новообразований [10] (рис. 1).
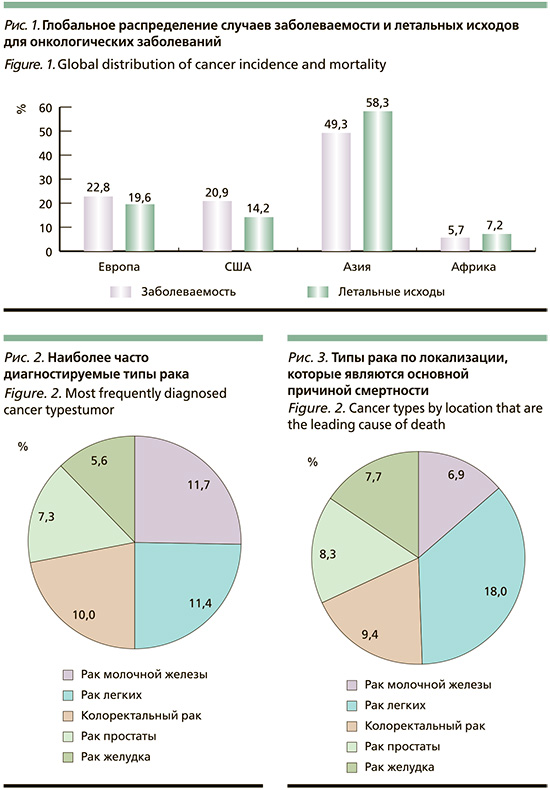
Более 60% новых случаев злокачественных новообразований и более 70% летальных исходов от них связывают с топ 10 наиболее распространенных типов рака и у мужчин, и у женщин.
Рак молочной железы возглавляет список наиболее распространенного онкологического заболевания у женщин. Далее по списку следует рак: легких, колоректальный, простаты и желудка, их вариабельность от общего числа случаев колеблется в пределах 5,6–11,7% (рис. 2) [10].
Список типов злокачественных новообразований по локализациям, вызывающих наиболее часто летальный исход возглавляет рак легких, далее колоректальный рак, рак печени, рак желудка и рак женской молочной железы, их вариабельность от общего числа случаев колеблется в пределах 6,9–18,0% (рис. 3) [10].
Наиболее часто встречающимся онкологическим заболеванием у мужчин является рак легких, далее следует рак предстательной железы и колоректальный рак, а также рак печени [10].
Различные подходы к лечению и их эффективность
Хирургия, лучевая терапия и химиотерапия признаны наиболее часто используемыми методами и предпочтительными во всем мире для лечения рака. В настоящее время совершенствуется и развивается таргетная терапия, фототермическая и фотодинамическая терапия. Однако индивидуализированное лечение рака все еще находится на начальной стадии [11].
Радиационное поражение, токсичность лекарств и другие побочные реакции могут возникнуть при традиционном лечении и даже привести к смерти, поэтому срочно необходимо расширять новые инструменты лечения злокачественных новообразований [11]. Однако лучевая терапия остается важным методом лечения рака, поскольку являются высокоэффективным мономодальным методом лечения, на который приходится лишь около 5% от общей стоимости лечения рака. Кроме того, примерно 50% всех больных раком будут получать лучевую терапию во время болезни, при этом, по оценкам, лучевая терапия способствует излечению примерно на 40%, а это достаточно хороший результат. Быстрый прогресс в этой области продолжает стимулироваться достижениями в методах визуализации, компьютеризированных системах планирования лечения, аппаратах лучевой терапии (с улучшенным производством рентгеновских лучей и проведением лечения), а также улучшенным пониманием радиобиологии лучевой терапии [12]. Радиация – это физический агент, который используется для разрушения раковых клеток. Используемое излучение называется ионизирующим излучением, поскольку оно образует ионы (электрически заряженные частицы) и откладывает энергию в клетках тканей, через которые проходит. Эта накопленная энергия может убить раковые клетки или вызвать генетические изменения, приводящие к гибели раковых клеток. Есть два способа доставить радиацию к месту расположения рака. Внешнее лучевое излучение осуществляется снаружи тела путем направления лучей высокой энергии (фотонов, протонов или частиц) на место опухоли. Это наиболее распространенный подход в клинической практике. Внутреннее облучение или брахитерапия осуществляется изнутри организма с помощью радиоактивных источников, запечатанных в катетеры или семена непосредственно в участок опухоли. Он используется, в частности, при рутинном лечении гинекологических заболеваний и злокачественных новообразований предстательной железы, а также в ситуациях, когда показано повторное лечение из-за его кратковременного эффекта [12]. Однако важно учитывать, что как химиотерапия, так и лучевая терапия часто сопровождаются выраженными побочными эффектами, включая гастроинтестинальную (до 90%), гематологическую (85–90%), гепатотоксичность (15–40%) и кардиотоксичность (до 50%). Эти осложнения могут значительно снижать качество жизни и переносимость лечения. В этой связи растет значимость нутритивной и детоксикационной поддержки как обязательной составляющей комплексного лечения пациентов с онкопатологией [13–18].
Иммунотерапия рака борется с ростом и инвазией опухолевых клеток, восстанавливая или стимулируя иммунную систему [11]. Иммунотерапия обычно включает цитокиновую терапию, блокаду иммунных контрольных точек, адаптивную клеточную иммунотерапию (adaptive cellular immunotherapy, ACT), противораковую вакцину, терапию онколитическим вирусом, клеточную терапию (cell therapy, CT) и конъюгат антитело-лекарственное средство (antibody-drug conjugate, ADC). Иммунотерапия, или концепция усиления иммунной системы для нацеливания и уничтожения раковых клеток, была способом лечения рака более 100 лет. Однако традиционная иммунотерапия добилась ограниченного успеха, поскольку раковые клетки имеют тенденцию развивать механизмы, которые ускользают от иммунного обнаружения. Для преодоления этого ограничения используется широкий спектр методов генной терапии [19].
В настоящее время генная терапия используется для создания рекомбинантных вакцин против рака. В отличие от вакцин против инфекционных агентов, эти вакцины предназначены не для предотвращения заболевания, а для его лечения или сдерживания, обучая иммунную систему пациента распознавать раковые клетки, предоставляя ей высокоантигенные и иммуностимулирующие клеточные остатки. Первоначально раковые клетки собирают у пациента (аутологичные клетки) или из установленных линий раковых клеток (аллогенные), а затем выращивают in vitro. Затем эти клетки конструируют так, чтобы они были более узнаваемы для иммунной системы, путем добавления одного или нескольких генов, которые часто представляют собой гены цитокинов, которые продуцируют провоспалительные иммуностимулирующие молекулы, или высокоантигенные белковые гены. Эти измененные клетки выращивают in vitro и уничтожают, а клеточное содержимое включают в вакцину. Также предпринимаются попытки иммунотерапии путем доставки иммуностимулирующих генов, главным образом цитокинов, в опухоль in vivo. Попав в раковую клетку, эти гены будут производить белки, которые демаскируют клетки от уклонения от иммунитета и способствуют выработке противоопухолевых антител [19].
В публикации Duong M.T. и соавт. [19] рассматриваются механизмы, с помощью которых бактерии нацеливаются на опухоли и подавляют их. Фундаментальным преимуществом бактериальной терапии рака является способность целенаправленно воздействовать на опухоли с помощью уникальных механизмов. В настоящее время считается, что бактерии проникают из кровообращения в опухолевую ткань как по пассивным, так и по активным механизмам [20]. Бактерии могут первоначально проникнуть в опухоль посредством пассивного захвата в хаотичной сосудистой сети опухоли, а затем проникнуть в опухоль вследствие воспаления, вызванного внезапным увеличением количества фактора некроза опухоли-α (TNF-α) в сосудах опухоли [20, 21]. Подвижность является важнейшим свойством, позволяющим бактериям проникать глубже в опухолевую ткань. В отличие от пассивного распространения и ограниченного проникновения, присущих химиотерапевтическим препаратам, бактерии представляют собой сложные живые организмы, которые могут получать энергию из окружающей среды; таким образом, их транспортная способность энтропийно неограничена. Помимо подвижности, иммунный ответ хозяина, по-видимому, влияет на распределение бактерий в опухолевой ткани [20].
Terrível M. рассматривает вопрос разработки онколитических вирусов, которые доставляются к местам опухоли, чтобы избирательно убивать опухолевые клетки и вызывать иммунный ответ против опухоли без серьезных побочных эффектов и риска выделения вируса. По мнению автора, онколитические вирусы имеют два основных различных и взаимодополняющих механизма действия: они действуют непосредственно, вызывая лизис или апоптоз опухолевых клеток, и косвенно, посредством стимуляции иммунной системы [22, 23]. Процесс проникновения вируса в клетку начинается со специфического связывания белков прикрепления вируса, находящихся на поверхности вируса, с определенным рецептором на поверхности клетки-хозяина. Эта специфичность определяет связь вируса с клеткой-хозяином определенного типа. В дальнейшем вирус проникает в клетку одновременно или с последующим снятием оболочки, что делает вирусный геном доступным для репликации. Наконец, после синтеза вирусных компонентов и сборки вириона вирусное потомство высвобождается из клетки посредством клеточного лизиса или экзоцитоза с намерением заразить другие клетки [22, 24]. В случае онколитической виротерапии предпочтительным является клеточный лизис, поскольку основной целью является уничтожение опухолевых клеток [22].
Особый интерес вызывают новые таргетные методы лечения. FDA уже одобрило некоторые таргетные противораковые препараты в последние годы, которые участвуют в блокировке путей биологической трансдукции и/или специфических раковых белков, вызывая гибель раковых клеток посредством апоптоза и стимуляции иммунной системы, или способности специфически доставлять химиотерапевтические агенты к раковым клеткам, сводя к минимуму нежелательные побочные эффекты [25]. В статье Pérez-Herrero Е. и соавт. [25] описаны прямые методы таргетной терапии путем изменения специфической клеточной сигнализации с помощью моноклональных антител или ингибиторов малых молекул, а также особое внимание уделяется непрямым таргетным подходам, которые в основном доставляют химиотерапевтические агенты к молекулярным мишеням, сверхэкспрессируемым на поверхности опухолевых клеток. Авторами рассматриваются вопросы о различных цитотоксических носителях лекарств, таких как липосомы, углеродные нанотрубки, дендримеры, полимерные мицеллы, полимерные конъюгаты и полимерные наночастицы, в пассивной и активной таргетной терапии рака путем повышения проницаемости и удержания или функционализации. Эти носители лекарств не только транспортируют химиотерапевтические агенты к опухолям, минуя нормальные ткани и снижая токсичность в остальной части организма, но также защищают цитотоксические препараты от деградации, увеличивают период полувыведения, полезную нагрузку и растворимость цитотоксических агентов и снижают почечный клиренс [25]. В условиях прогресса молекулярной и визуальной диагностики параллельно развиваются и подходы к коррекции метаболических нарушений, обусловленных как самим опухолевым процессом, так и его лечением. Особенно актуально это в контексте энергетического и нутриентного дефицита, возникающего на фоне токсичности терапии. Исследования показывают, что нутритивная поддержка с использованием специализированных энтеральных продуктов (например, «ЛЕОВИТ ONCO») позволяет снизить выраженность симптомов интоксикации, уменьшить частоту побочных эффектов и улучшить показатели качества жизни пациентов [14–18, 26–33].
Прогресс в диагностике онкологических заболеваний
Диагностика и классификация рака традиционно основываются на гистологическом исследовании. Однако этот подход создает проблемы, связанные с инвазивным сбором ткани, невозможностью различить клинически значимые подтипы рака, а также вариабельностью между и внутри наблюдателя. В ответ на эти недостатки появились новые высокопроизводительные платформы с целью лучшей характеристики рака на молекулярном уровне, позволяющие ставить более ранний диагноз, лучшую стратификацию и более точный прогноз, чем гистопатологические подходы для таргетного лечения. В этом сценарии технологические усовершенствования в области визуализации и молекулярной биологии привели к «радиогеномике» или «визуальной геномике». Концепция радиогеномики заключается в возможности исследовать взаимосвязь между визуализацией, геномикой и клиническими знаниями, просто рассматривая данные, независимо от какой-либо качественной интерпретации. Таким образом, радиогеномные подходы в значительной степени основаны на численных расчетах и компьютерных методах, что позволяет управлять и анализировать очень большое количество переменных для каждого образца и модальности. Например, изображение онкологического поражения обычно оценивается радиологом по функциональным/морфологическим признакам (шиповидное, усиленное, гиперинтенсивное, очаговое, глюкозо-зависимое), но само исследование визуализации является многомерным источником данных; поэтому основная цель радиогеномики – извлечь значимую информацию непосредственно из данных [34].
Секвенирование нового поколения (Next generation sequencing, NGS), также называемое массовым параллельным секвенированием, было разработано лишь недавно и позволяет запускать процессы секвенирования для миллионов фрагментов ДНК без предварительного знания последовательности. Данная технология является революцией в мире молекулярной биологии, так как ускорила и удешевила процесс секвенирования в сотни тысяч раз. Некоторые виды рака имеют семейную предрасположенность, а специфические генные мутации повышают риск развития этого заболевания в течение всей жизни. За последние десятилетия основа такой генетической предрасположенности была выяснена для нескольких синдромов рака, а гены с высоким риском, мутировавшие в семейных случаях, в настоящее время подвергаются программам генетического диагностического скрининга. Тестирование мутаций в этих генах оказывает большое влияние на генетическое консультирование, помогает повысить шансы на выживание, определяет прогноз носителей и наиболее подходящие и персонализированные профилактические меры. Кроме того, в некоторых странах носители мутаций могут выбрать экстракорпоральное оплодотворение (IFV) с предимплантационной генетической диагностикой (ПГД), чтобы предотвратить передачу мутации их потомству [35].
Заключение
Таким образом, несомненным остается факт ежегодного роста онкологических заболеваний. По данным, представленным в открытом доступе, лишь на 2021 г. 3 940 529 человек являются пациентами с установленным диагнозом злокачественного новообразования, 278 992 человек умерло от злокачественных новообразований на 2021 г. лишь в России. О чем это говорит? С одной стороны, о том, что рак прогрессирует и идет семимильными шагами, факторы, повышающие риск возникновения онкологии, находят все большее место в нашей обыденной жизни, к ним относятся и экологические проблемы, вредные привычки, нездоровый образ жизни и психологический климат в мировом сообществе, но в то же время научное сообщество не стоит на месте, и, возможно, повышение диагностируемости онкологических заболеваний также связано с улучшением уровня диагностики, внедрением новых технологий в диагностику, таких как NGS технологии и методов радиогеномики, с повышением уровня предоставляемой терапии. Ведь теперь выбор терапии при обнаружении злокачественных новообразованиях куда выше, чем раньше, и не сводится лишь к хирургии и лучевой терапии. Технические и биоинформационные достижения в онкологии позволяют врачам и технологиям не стоять на месте и развиваться. Крайне важно, чтобы этот прогресс сопровождался растущим осознанием его большого потенциала врачами и пациентами. Также принципиально важно, чтобы прогресс сопровождался строгим контролем за использованием этих технологий с точки зрения этических вопросов и сохранением баланса между надеждой и ажиотажем. Таким образом, современные тенденции в лечении онкологических заболеваний направлены не только на совершенствование методов диагностики и терапии, но и на поддержание метаболического гомеостаза, включая контроль за оксидативным стрессом, коррекцию нутритивного дефицита и профилактику интоксикации. Применение специализированного питания, как показывают клинические исследования, представляет собой эффективный элемент персонализированной поддержки пациентов, повышающий их шансы на успешную реабилитацию и ремиссию.



